...
| Table of Content Zone | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||
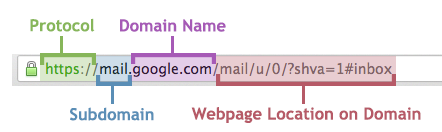
Parts of a Web AddressThe trick to avoiding spoofed webpages is the web address, also known as the URL. People who phish may be able to duplicate everything about the way a webpage looks, but a web address can't be duplicated. A web address is divided into four parts: protocol, subdomain, domain name, and webpage location. People who phish manipulate these parts in order to make their websites look legitimate. If any of these parts look suspicious, you shouldn't enter any personal information, such as usernames or passwords, into the website. ProtocolThe protocol tells a web browser how to send and receive data. The most common protocol is http or https. You'll see https on secure Secure pages, such as login pages, will use https because it ensures your browser encrypts your information and prevents people who phish from grabbing the data as it's transferred. Secure PSU pages will always begin with HTTPS and a lock symbol. Any page that looks like a PSU login page but doesn't use HTTPS and doesn't have a lock symbol is suspicious and should be approached with cautionSometimes the protocol is hidden in a web browser’s address bar. Select the URL and the protocol will display. Look For The LockSecure PSU pages will always display a padlock icon to the left of the URL. Any page that looks like a PSU login page but doesn't have a padlock icon is suspicious and should be approached with caution. SubdomainThe subdomain indicates a subdivision of the webpage's domain. For instance, in the web address "mail.google.com", "mail" is the subdomain of "google.com". PSU has a number of subdomains, such as "mail.pdx.edu" and "d2l.pdx.edu". People who phish may attempt to use a subdomain to make the link seem official. Check to make sure that the web address isn't using a PSU-related subdomain with a non-PSU domain name (see below for examplessome examples are in the next section). This could indicate that a someone is trying to trick you into trusting a fake PSU webpage.. Domain NameThe domain name is a unique identifier that differs for every website on the internet. A domain name always includes a top-level domain, which is most commonly ".com", but can also be ".org" or, in PSU's case, ".edu". People who phish will often try to fake this part of a web address by creating something that looks very similar. For instance, they might create a domain name that uses a 0 (the number) in place of an O (the letter) or has a ".co" instead of a ".com". Check the domain name to ensure that you are on a legitimate PSU website: it should always show "pdx.edu" immediately after the protocol and the subdomain. Webpage Location on DomainEverything after the domain is information regarding the page's location. This information is usually not necessary to examine. If you're unsure whether the web address looks legitimate, go straight to the website by typing its web address in yourself. Further ResourcesIf you believe you've received a phishing email, do not click on follow any of the links in it. Instead, forward it to to abuse@pdx.edu. Related Articles
|
...